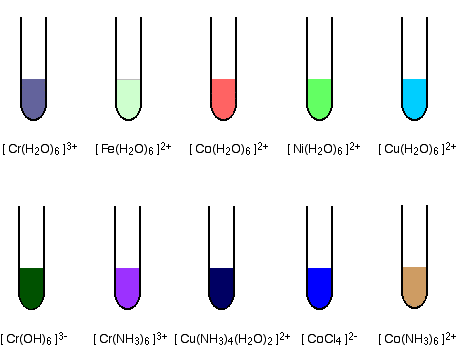
Colours Of Transition Metals. Colour of Transition metals. Titanium forms some titanium III compounds containing the Ti3 ion which are usually blue-violet in colour. Not all transition metal compounds are coloured. The same charge on a metal ion may produce a different color depending on the ligand it binds.
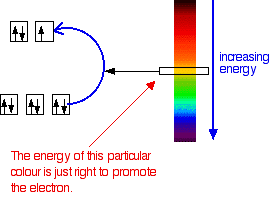
These can most easily occur when the metal is. The transition metals have certain colours or colour ranges that are typical of that metal. The specific ligands coordinated to the metal center also influence the color of coordination complexes. Most transition metal colours are due to d-d electron transitions. Copper salts for example are usually blue or green iron has salts that are pale green yellow or orange. When transition metals in low oxidation states are in alkaline solution they are more easily oxidised than when in acidic solution CrH2O63aqCrOH 6.
Another factor is the chemical composition of the ligand.
Transition metal ions The corresponding transition metal ions are coloured. On the other hand coordination compounds of transition metals with weak-field ligands are often blue-green blue or indigo because they absorb lower-energy yellow orange or red light. Colour in transition-series metal compounds is generally due to electronic transitions of two principal types. As shown in the graphic above different charges on the same transition metal can also accomplish this. These can most easily occur when the metal is. In transition metal complexes the colours are usually due to electrons hopping among d-orbitals.